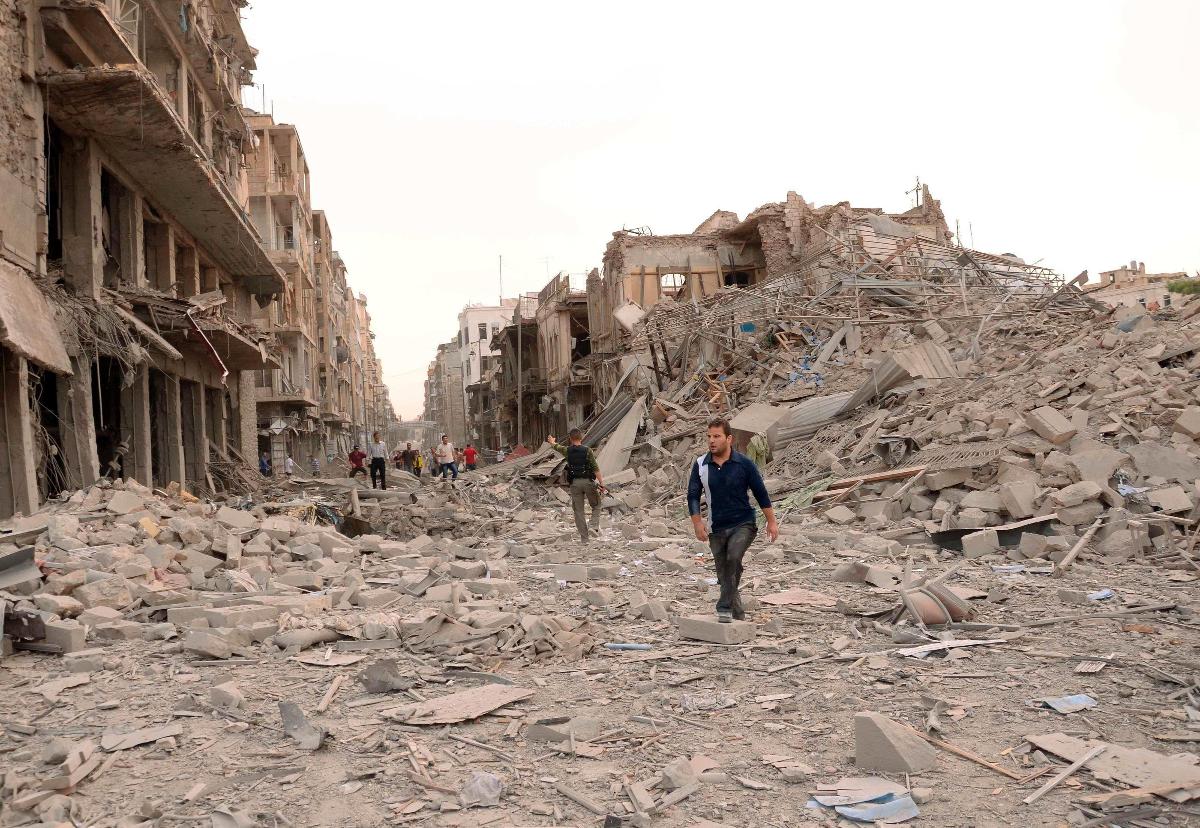
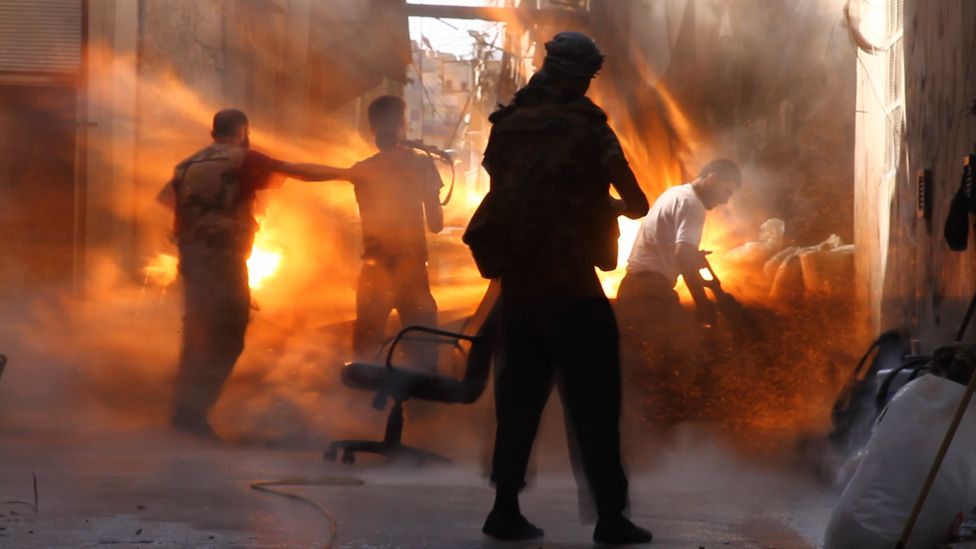
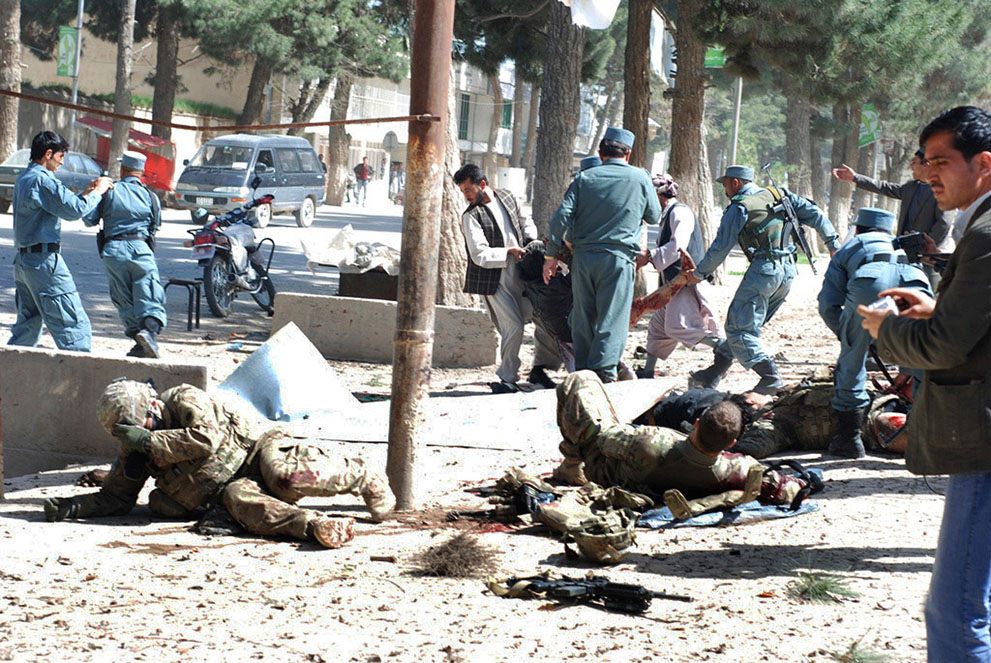
Beirut, Sarajevo, Grozny, Baghdad, and now Aleppo. When it comes to the senseless destruction of cities, no one even makes the pretense to say “Never Again.” After all, they can be rebuilt, can’t they? Look at how Europe was rebuilt after World War II. But that was then: not just a different war, but a different conception of war and of peace. Today, war’s destructiveness is both less widespread and more continuous. Destruction seems to have found a different role in the historical process, and war produces not new world orders but rather more localized forms of sustainable catastrophe. If so, an outline of this shift in the nature of things might be evident in a photo such as this one.
A few people walk through what remains of Aleppo’s main Saadallah al-Jabari Square after a bombing. But don’t think for a minute that this scene is particularly unique or dramatic. There are hundreds of photos of other streets in Aleppo and elsewhere in Syria and elsewhere around the globe. The media coverage long gone, most of them are now part of a story no one wants to cover: decaying infrastructure, abandoned tanks and burnt-out trucks used as makeshift playground equipment, people coping as best they can with little outside investment and not much to hope for. Where once they lived in vibrant communities, now they live among the ruins in Rubble World.
I first wrote about Rubble World in 2008, and not much has changed for the better since then. Even with the Arab Spring, it can often seem that the swath of destruction is not so much the temporary cost of progress but rather a harbinger of even more gun running and militia violence. Instead of seeing the expansion of civil society–although that, too, is part of the historical struggle–the promise of a better life is betrayed to some strange combination of international networks and clan politics. Whatever the mix, the priorities don’t often involve rebuilding the cities.
Of course, people are much more important than property, and the many images of Syrians being killed–among the several hundred killed every day–are rightly a more salient and more effective witness to the tragedy that is unfolding slowly and painfully. (See, for example, the first image here.) But I also find these images of concrete desolation to be moving. No one cries for concrete, but the built environment is both substance and symbol of urban community. (So it is, for example, that both architecture and graffiti prompt public debate.) War harms both individuals and communities. An individual can lose a limb or a loved one, and a city can lose its culture and its future.
So it is that an image of the present may double as a glimpse into where civilization is headed. It can’t tell the whole story, of course, but it can suggest how one possible pathway is already coming into existence. I almost said, already being built, but it may not exactly work that way. The future may involve a particularly perverse form of creative destruction: one in which the new city is being created by the same process that is destroying the old one.
Photograph by George Ourfalian/Reuters.