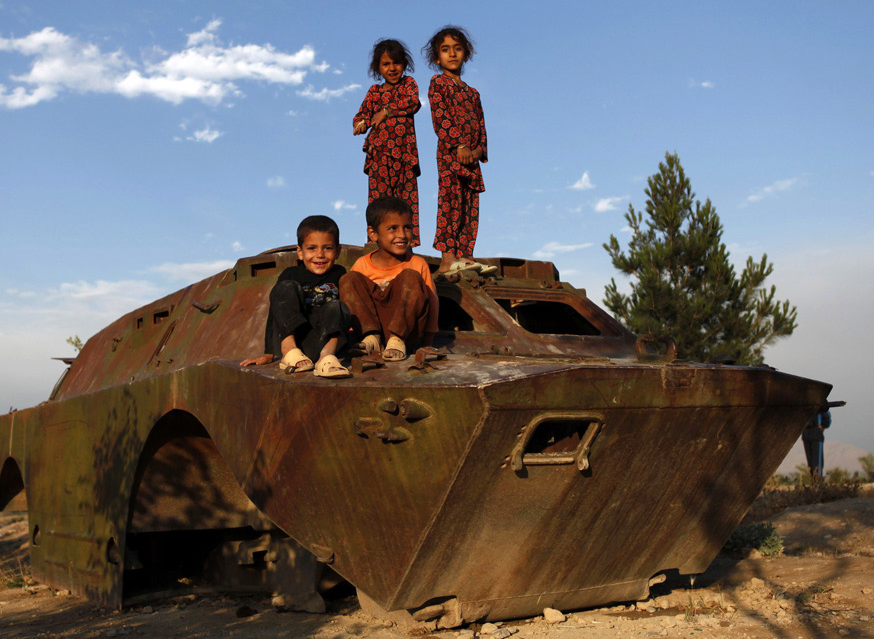
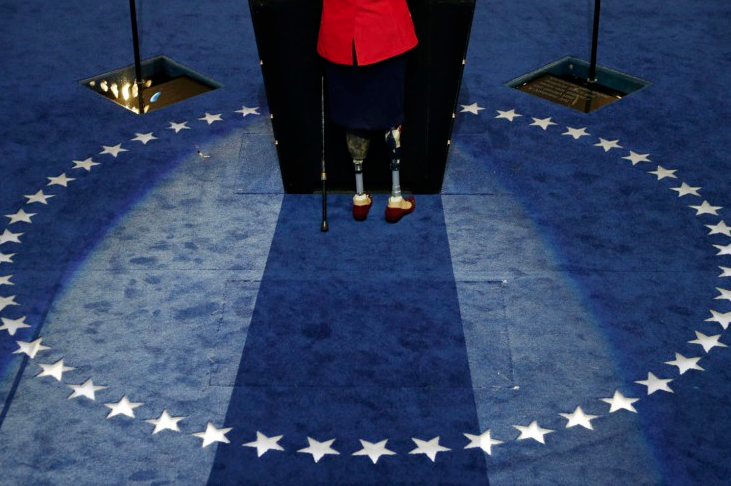
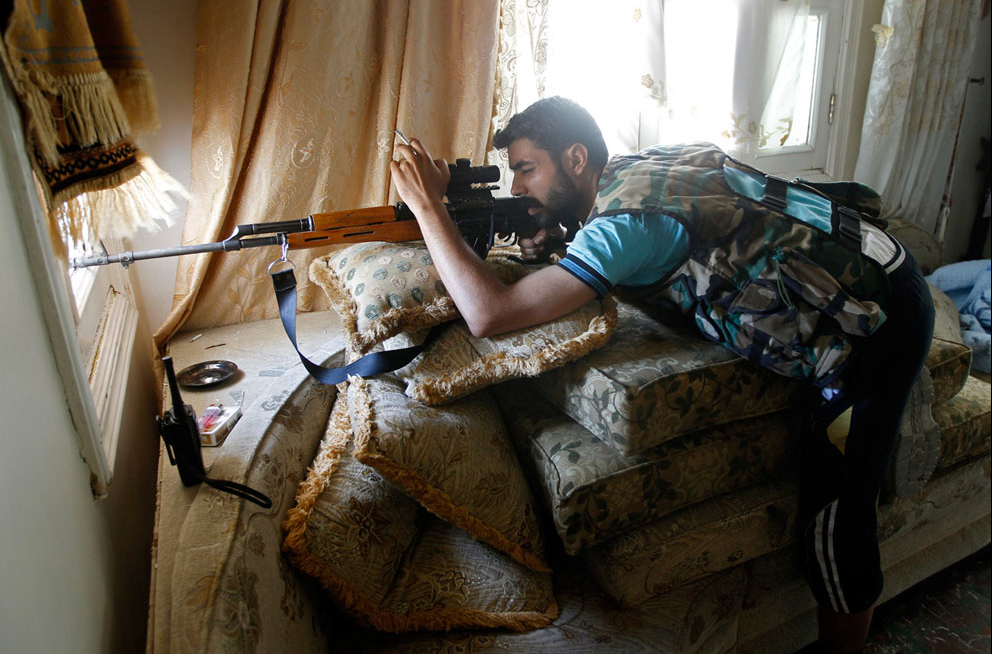
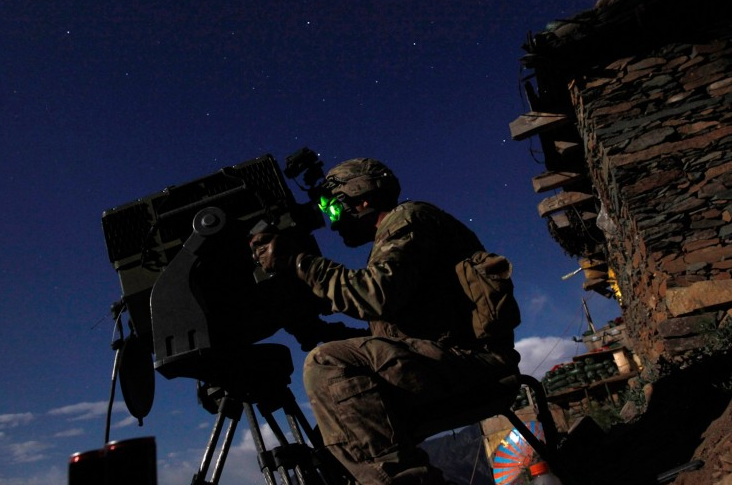
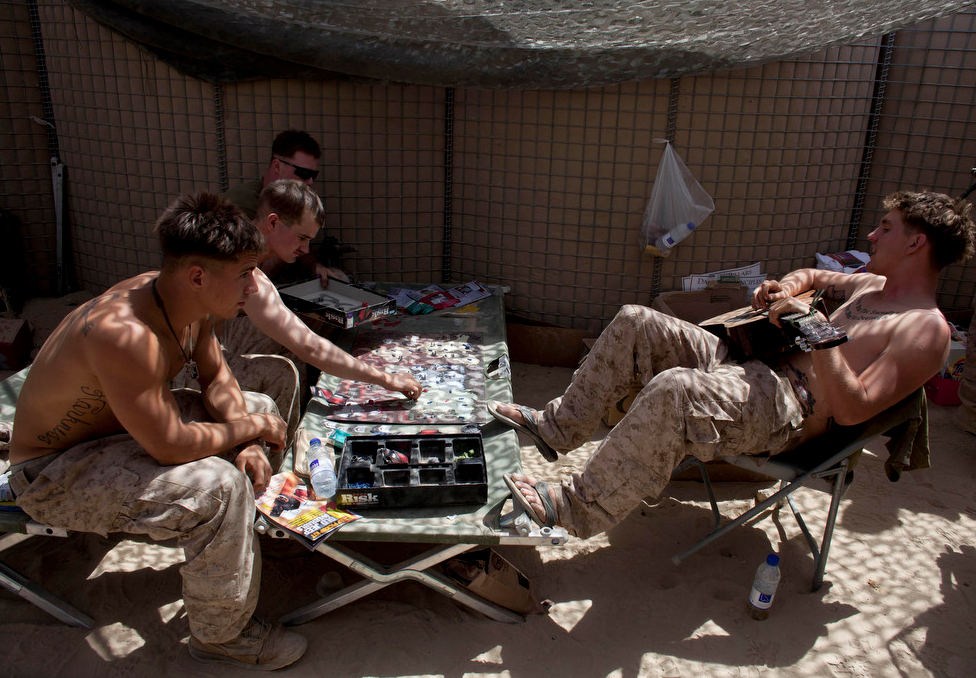
The point of comparison is apparent. The visual quotation is to what is arguably one of, if not the, most famous, recognizable, and reproduced photographs in all the world. And more, it is the photograph most often pointed to as the icon of “the good war,” a total war fought against unregenerate, totalitarian evil in the name of freedom and democracy. And what made that photograph taken in February, 1945 so incredibly powerful was the way in which it transcribed and coordinated commitments to egalitarianism, an embodied sense of nationalism, and a civic republican ethos within a single image. What makes the photograph above so distinct—and in its own way quite important—is how, despite its obvious gesture to the original, it resists or erases everyone of the original three transcriptions.
The Iwo Jima photograph depicts the war effort as essentially egalitarian. We see six men, all wearing identical uniforms, with no indication of rank, engaged in common labor for a common goal. They are a working class equal to the task because they are working equal alongside one another, no one straining more than another, no one more at risk than another. The sacrifice is thus collective, the individual subordinated to the common good. In its way, the egalitarianism of the photograph modeled the egalitarianism of the overall war effort, not just on the battle front, but on the home front as well, where rationing, Victory gardens, and the purchase of war bonds were the order of the day. But in the photograph above, shot at Camp David in the Helmand province of Afghanistan, there is no egalitarianism because there are no equals. Instead of a collective effort to raise the flag we have a single individual struggling against the wind to put the standard in place. The effort and the sacrifice are solitary. He alone does the job. And if the photograph gestures to the original icon of the “good war,” where the sacrifice was egalitarian, it also points here by implication to a war fought by individuals rather than by the nation as a whole. Perhaps that is why he seems to struggle so hard and why it is not altogether clear that he will overcome the force that opposes him.
References to the nation here are not incidental, for in the iconic image the commitment to egalitarianism was inflected by a pronounced appeal to nationalism. It is notable that captions for the original photograph emphasized “Old Glory” or “the flag,” underscoring the symbolic significance of the standard being raised. As one of the original flag raisers commented years later, “You think of that pipe. If it was being put in the ground for any other reason … Just because there was a flag on it, that made the difference.” The caption for the above photograph, however, virtually ignores the national significance of the flag itself, as it notes that “U.S. Army SPC Jeremy Stocks … restores a flagpole back in place after the flagpole fell in a night sandstorm (emphasis added).” The flag is there, to be sure, but it is reduced in significance to the pole itself; the banner could symbolize anything as far as the caption is concerned—a regiment for example—and it would not seem to matter to the task at hand. But there is more, for you will no doubt recall that in the original photograph the flag raisers were turned away from the camera, leaving “Old Glory” as the face of the image. Indeed, it was not insignificant in this regard that the flag raisers were initially anonymous and thus capable of standing in for an anonymous national public. But here the flag raiser’s face is fully recognizable and he even has a name. The opportunity for collective or national identification is thus doubly removed.
Appeals to nationalism typically operate in an heroic register, and in the U.S. this often manifests itself in a civic republican style that emphasizes (among other things) monumental sacrifices by ordinary people. The Iwo Jima photograph manifests this larger than life heroism with its monumental outline and sculptural qualities, the massed figures cast as if cut from stone, powerful yet immobile. No doubt these features and their corresponding sense of “timelessness” made for such strong extension into posters, war bond drives, and, of course, a memorial statue. And one can see how this was achieved visually. In typical reproductions of the original photograph the scene is cropped vertically, as if a portrait, and shot slightly from below; the effect is to magnify the flag raisers against the scene which they dominate. Contrast this with the more recent photograph, cropped horizontally, as if in a landscape, and shot on a more or less level plane; the corresponding effect is to minimize the flag raiser who is now dwarfed by a scene dominated by the sky and the flag pole.
The scene, of course, sets the stage for action, and here, once again, the caption is telling, as it describes the lone flag raiser as fighting against the wind. It is not insignificant in this regard that in the Iwo Jima photograph the wind is to the back of the flag raisers, thus evoking the sense in which nature—and perhaps, by extension, providence—is on their side. Here nature is the enemy, and again, perhaps, with all that that entails. But more to the point, there doesn’t seem to be anything particularly heroic about replacing a flag pole knocked down by a sandstorm. If anything, the effort here seems more futile than monumental. Indeed, it is hard to shake the thought that this flag pole isn’t destined to be knocked down by many more sandstorms in the future. It is certainly hard to imagine anyone ever using this photograph as the template for a statue to memorialize the war.
It would be easy to conclude that the image above is the cynic’s answer to the war in Afghanistan, the longest war in U.S. history by a factor of two and going strong. And we should not be too quick to exclude that possibility or its implications. But at the same time we should be careful to take account of how our representations and remembrances of the “good war”—a war that ended in atrocity with the dropping of two nuclear bombs—goads the ways in which we think about our place in the world and thus inclines us to impose our own, idealized egalitarianism, nationalism, and civic virtue on other peoples.
Photo Credit: Denis Sinyako/Reuters
1 Comment